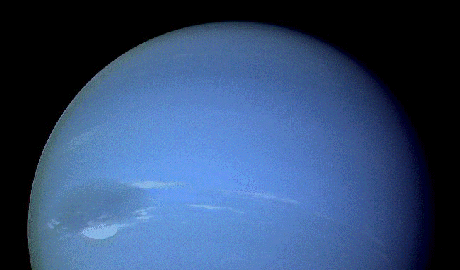
 Neptune
Neptune
The Mystic
Neptune Facts
- Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun
and the fourth largest (by diameter):
- distance from Sun: 4,504,000,000 km (30.06 AU)
- equatorial diameter: 49,528 km; polar diameter: 48600 km
- mass: 1.0247e26 kg
Neptune is smaller in diameter but larger in mass than
Uranus.
- In Roman mythology Neptune (Greek:
Poseidon)
was the god of the Sea.
- After the discovery of Uranus, it was noticed that its orbit was not as it
should be in accordance with Newton's laws.
It was therefore predicted that another more distant planet must be
perturbing Uranus's orbit. Neptune was
first observed by Galle in 1846
in exactly the spot independently predicted by
Adams and
Le Verrier
from calculations based on the observed
positions of Jupiter,
Saturn and Uranus.
An international dispute arose between Adams and Le Verrier over priority
and the right to name the new planet;
they are now jointly credited with Neptune's discovery.
Subsequent observations have shown
that the orbits calculated by Adams's and Le Verrier's diverge from Neptune's
actual orbit fairly quickly. Had the search for the planet taken place a few
years earlier or later it would not have been found anywhere near the predicted
location.
- Neptune has been visited by only one spacecraft,
Voyager 2 on Aug 25 1989.
Almost everything we know about Neptune comes from this encounter.
- Because Pluto's orbit is so eccentric,
it sometimes crosses the orbit of
Neptune. Since 1979 Neptune has actually been
the most distant planet from the Sun; Pluto will again be the most distant in
1999.
- Neptune's composition is probably similar to Uranus's: various
"ices" and rock with about 15% hydrogen and
a little helium.
Like Uranus, but unlike Jupiter and Saturn, it seems not to have a distinct
core but rather to be more or less uniform in composition.
Its atmosphere is mostly hydrogen and helium with a small amount of methane.
- Neptune's blue color is the result of absorption of red light by methane in the
atmosphere.
- Like a typical gas planet, Neptune has
rapid winds confined to bands of latitude and large storms or vortices.
Neptune's winds are the fastest in the solar system, reaching 2000 km/hour.
- Like Jupiter and Saturn, Neptune has an internal heat source -- it radiates about
twice as much energy as it receives from the Sun.
- At the time of the Voyager encounter,
Neptune's most prominent feature was
the Great Dark Spot (picture 18).
It was about half the
size as Jupiter's Great Red Spot (about the
same diameter as Earth). Neptune's winds blew the Great Dark
Spot westward at 300 meters/second (700 mph).
Voyager 2 also saw a small irregular
white cloud that zips around Neptune every 16 hours or so now known as
"The Scooter". It may be a plume rising from lower in the atmosphere
but its true nature remains a mystery.
- However, HST observations of
Neptune (picture 25) in 1994
show that the Great Dark Spot has disappeared! It has either simply
dissipated or is currently being masked by other aspects of the atmosphere.
A few months later HST discovered a new dark spot in Neptune's northern
hemisphere. This indicates that Neptune's atmosphere
changes rapidly (picture 26), perhaps
due to slight changes in the temperature differences between the tops and bottoms
of the clouds.
- Neptune also has rings.
Earth-based observations showed only faint arcs instead
of complete rings, but Voyager 2's
images showed them to be complete rings with bright clumps
(pictures 22, 23).
- Like Uranus and Jupiter, Neptune's rings are very dark but their composition is
unknown.
- Neptune's magnetic field is, like Uranus's, oddly oriented and probably generated
by motions nearer the surface than the center of the planet.
- Neptune can be seen with binoculars (if you know exactly where to look) but a large
telescope is needed to see anything other than a tiny disk.
Mike Harvey's planet finder charts show the current position of Neptune (and the other planets) in the sky, butmuch more detailed charts will be required to actually find it.
Pictures
- (above) Full Disk Neptune
93k gif;
29k jpg;
186k gif
- Neptune
291k gif
- Thin Crescent of planet Neptune
162k gif
- Parting view of Neptune and moon Triton
59k gif;
17k gif;
23k jpg
- Neptune in false color
158k gif;
210k gif
- Neptune in thin crescent, south view (B&W)
160k gif
- Far view of Neptune showing clouds (B&W)
30k gif
- Rise of Triton on Neptune (B&W)
23k gif
 Scooter with Spots
88k gif;
68k jpg
Scooter with Spots
88k gif;
68k jpg
- Cloud Evolution
58k gif;
25k jpg
- Bright Cloud Streaks
140k gif;
29k jpg
- Clouds in Neptune's atmosphere (B&W)
199k gif
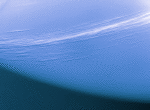 Cirrus-like clouds
195k gif
Cirrus-like clouds
195k gif
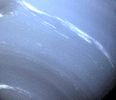 wave structures?
63k jpg
wave structures?
63k jpg
- Zoom on clouds (B&W)
202k gif
- Small Dark Spot
190k gif;
133k jpg
- Small Dark Spot
116k gif
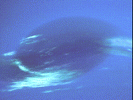 The Great Dark Spot
423k gif;
153k gif;
97k jpg
The Great Dark Spot
423k gif;
153k gif;
97k jpg
- Neptune's Great Dark Spot
126k gif
- Dark Spot and Scooter
114k gif
- Big spot of Neptune with the 'scooter' (B&W)
38k gif
63k gif;
10k jpg
- Rings
89k gif
 Twisted Rings
77k gif;
43k jpg;
246k gif
Twisted Rings
77k gif;
43k jpg;
246k gif
- Neptune's Rings (B&W)
172k gif
- HST images of both hemispheres
33k jpg;
146k gif;
caption
 HST images
25k jpg;
108k gif
HST images
25k jpg;
108k gif
- ... more Neptune images
Movies
- Ring Arc Closeup
1334k quicktime
- Neptune in Rotation
2800k AVI
- Neptune's Dark Spot
1100k AVI
Neptune's Satellites
Neptune has 8 known moons; 7 small ones and Triton.
Distance Radius Mass
Satellite (000 km) (km) (kg) Discoverer Date
--------- -------- ------ ------- ---------- -----
Naiad 48 29 ? Voyager 2 1989
Thalassa 50 40 ? Voyager 2 1989
Despina 53 74 ? Voyager 2 1989
Galatea 62 79 ? Voyager 2 1989
Larissa 74 96 ? Voyager 2 1989
Proteus 118 209 ? Voyager 2 1989
Triton 355 1350 2.14e22 Lassell 1846
Nereid 5509 170 ? Kuiper 1949
Distance Width
Ring (km) (km) aka
------- -------- ----- -------
Diffuse 41900 15 1989N3R
Inner 53200 15 1989N2R
Plateau 53200 5800 1989N4R
Main 62930 < 50 1989N1R
(distance is from Neptune's center to the ring's inner edge)
More about Neptune and its satellites
Open Issues
- Neptune's magnetic field is off center and at a large angle to its rotation axis.
What processes in the interior generate this oddly shaped field?
- What accounts for the relative lack of hydrogen and helium in Neptune (and
Uranus)?
- What happened to the Great Dark Spot?
 ... Sun
... Uranus
... Oberon
... Neptune
... Naiad
... Pluto
...
... Sun
... Uranus
... Oberon
... Neptune
... Naiad
... Pluto
... 

Bill Arnett; last updated:
1995 July 26

 Scooter with Spots
88k gif;
68k jpg
Scooter with Spots
88k gif;
68k jpg
 Cirrus-like clouds
195k gif
Cirrus-like clouds
195k gif
 wave structures?
63k jpg
wave structures?
63k jpg
 The Great Dark Spot
423k gif;
153k gif;
97k jpg
The Great Dark Spot
423k gif;
153k gif;
97k jpg
 Twisted Rings
77k gif;
43k jpg;
246k gif
Twisted Rings
77k gif;
43k jpg;
246k gif
 HST images
25k jpg;
108k gif
HST images
25k jpg;
108k gif